Commonly Encountered Aromatic Compounds
Structure
Name
Structure
Name
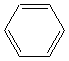
Benzene
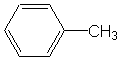
Toluene
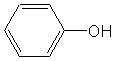
Phenol
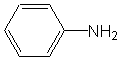
Aniline
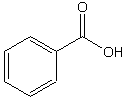
Benzoic acid
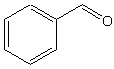
Benzaldehyde
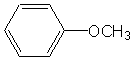
Anisole
Methyl phenyl ether
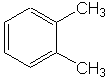
o-Xylene
For compounds containing more than one group attached to the benzene ring, compounds are named using the parent molecule (e.g., aniline, toluene, phenol, etc.) as the root name, and the other attached group relative to the parent. For benzene derivatives, the prefixes, ortho (o), meta (m), and para (p) are used, instead of 1,2 or 1,3 or 1,4 attachment positions, respectively. As an example, 1,2-xylene is o-xylene (shown above), 1,3-xylene is m-xylene, and 1,4-xylene is p-xylene. Likewise, 1,2-nitrotoluene is o-nitrotoluene, 1,3-nitrotoluene is m-nitrotoluene, and 1,4-nitrotoluene is p-nitrotoluene.