Stops 2a and 2b
Miocene Volcanic Unit, Local
Faulting
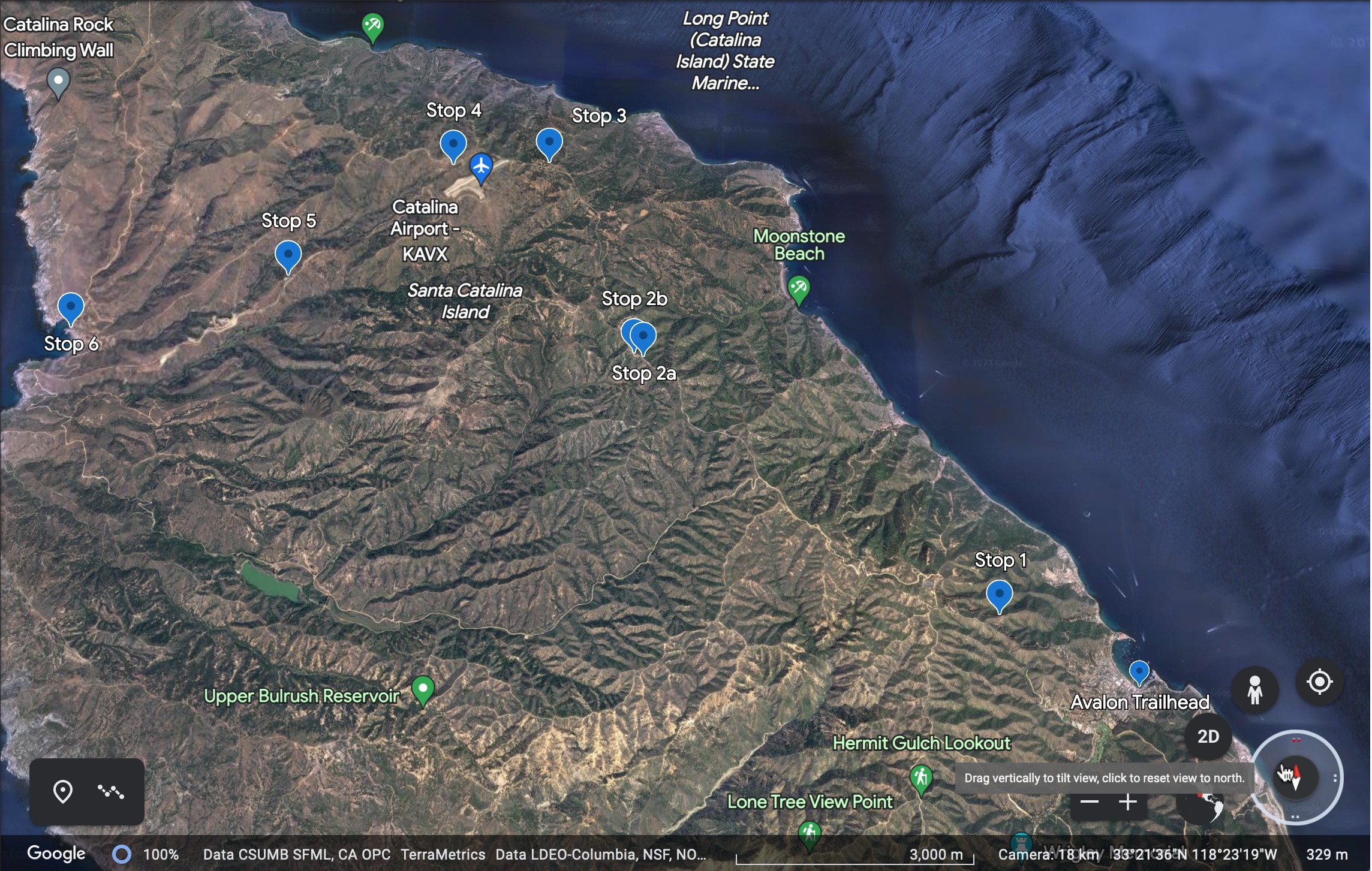
Stop 2 is northwest of Stop1. (Google Earth)
Stop
2a
Here we see tilted volcanic sequences, separated by
paleosols. A paleosol is an existing soil surface thatís gets overlain by a
volcanic flow. The Miocene volcanics are extrusive they have come to the
surface and cooled quickly. The color change (becomes darker) is apparent along
the highway when crossing into the volcanics. The unit is mainly andesite flows
and flow breccias, but the composition ranges from basalt to rhyolite. There
are many dikes and dike swarms that crosscut larger massive rock units.
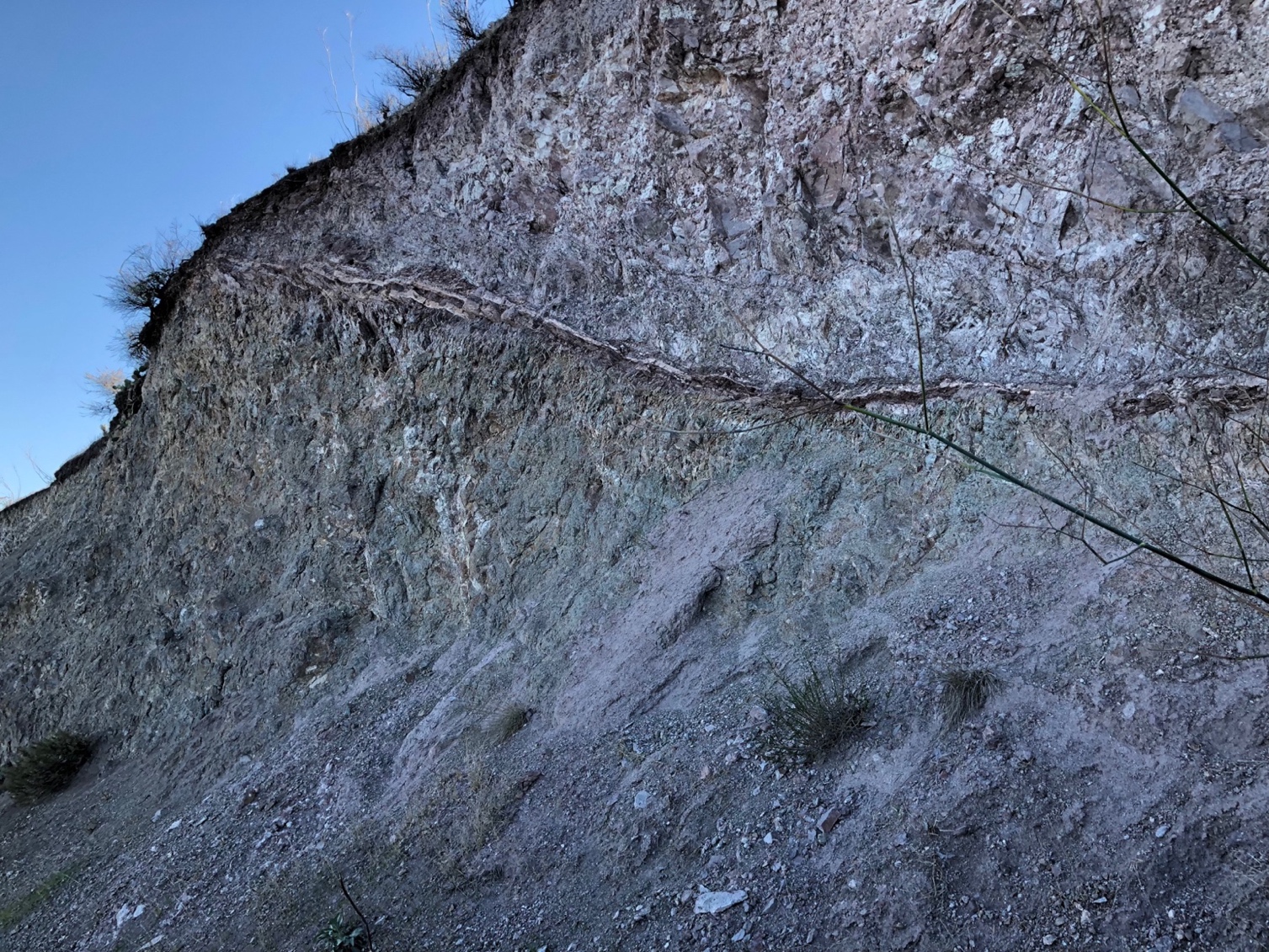
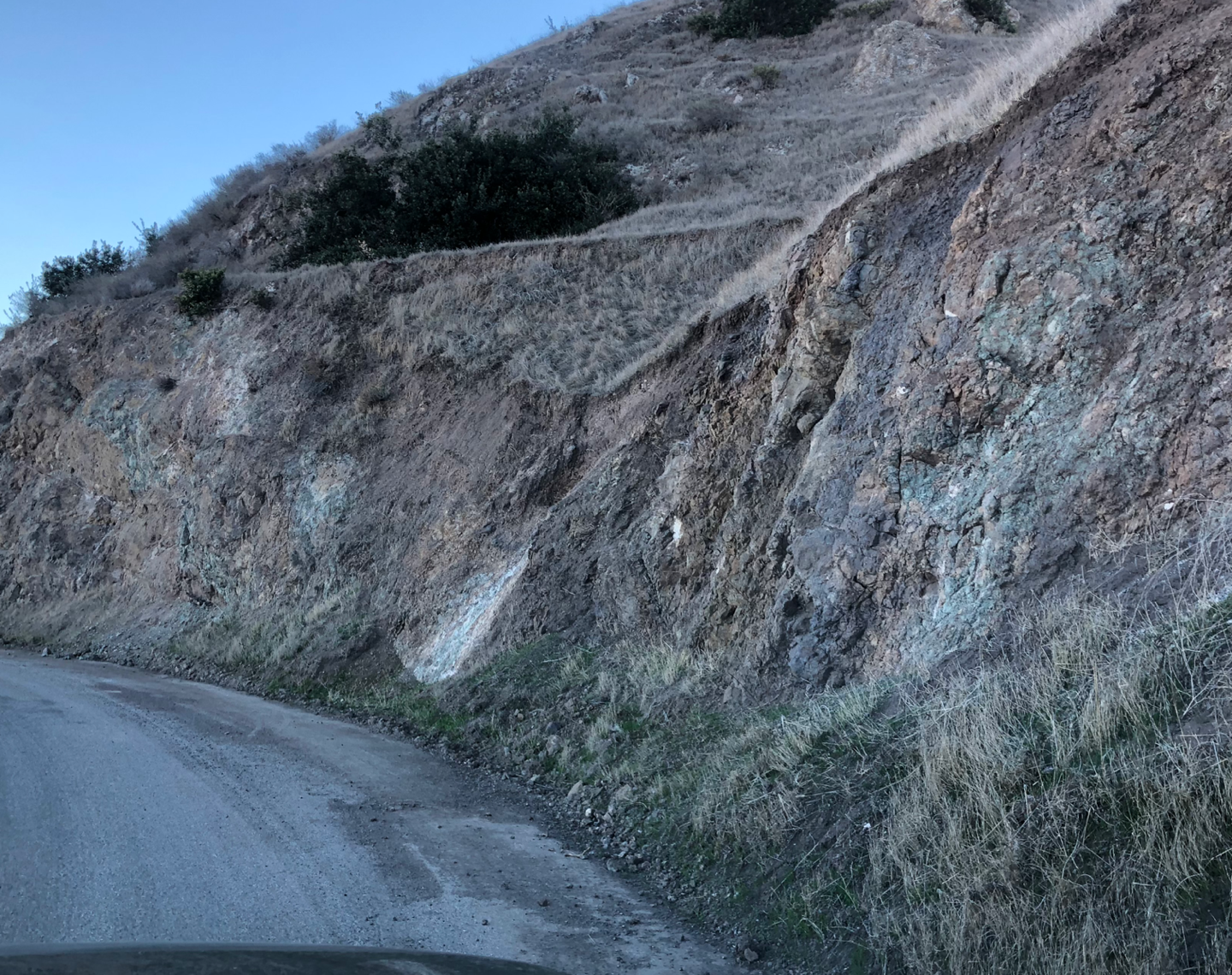


The
volcanic unit, note the paleosol (old soil surface running across the first
photo). You can see the color (and probably composition) change above and below
it. Note the colors in the outcrop, its common to see a wide range of colors
like greens and purples in volcanic rocks.
Stop 2b
In the field geologists often use vegetation to map geologic changes in the rocks. In this example, the fault has vegetation growing directly in it. Faults are often water conduits, so vegetation likes to grow in or on them. You can see this is on all scales in the field.
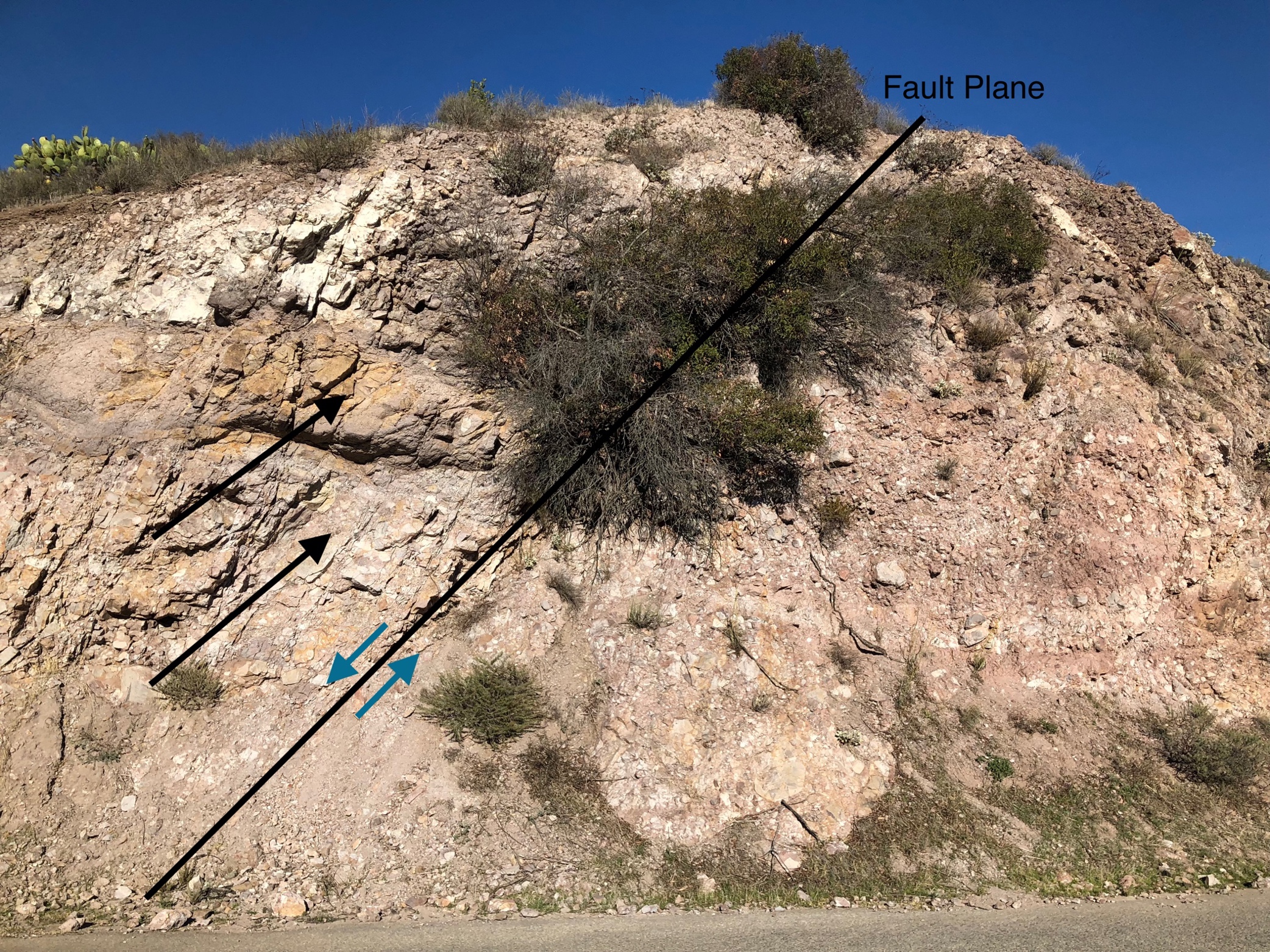

The
green arrows (small on fault plane) show the relative movement on the fault.
The large black arrows show beds that are offset across the fault, they are not
apparent on the other side. This is a normal slip fault caused by tension.

Another video of
Humpback whales in schools of dolphin and yellowfin tuna, on the shuttle
from Dana Point to Avalon October 2023.